Exploring the intricate relationship between stress and hormonal health, this article delves into the impact stress can have on your body's delicate balance of hormones. From cortisol to sex hormones, we uncover how stress influences various aspects of your hormonal well-being.
Introduction to Hormonal Health and Stress
Hormonal health plays a crucial role in maintaining various functions within the body. Hormones act as messengers, regulating processes such as metabolism, growth, mood, and reproduction. When these hormones are imbalanced, it can lead to various health issues.
Stress is the body's response to any demand or threat, triggering a cascade of physiological reactions. While stress is a natural response, chronic stress can have detrimental effects on the body, including disrupting hormonal balance.
Relationship Between Stress and Hormonal Balance
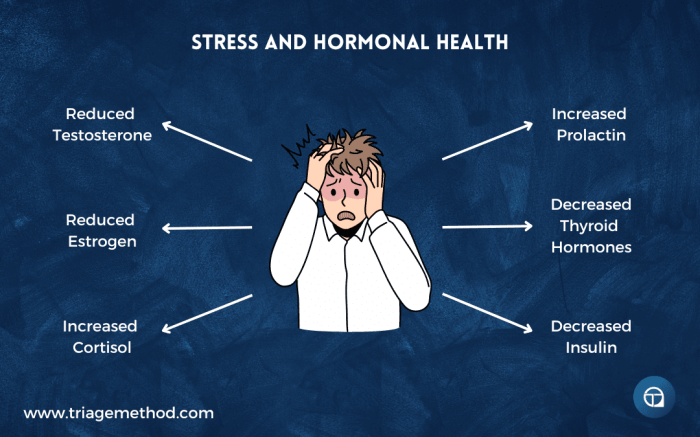
Stress can impact hormonal balance in several ways:
- Cortisol: Known as the stress hormone, cortisol levels can rise significantly during stressful situations, affecting other hormones in the body.
- Thyroid Hormones: Chronic stress can interfere with the production of thyroid hormones, which regulate metabolism and energy levels.
- Reproductive Hormones: Stress can disrupt the balance of reproductive hormones, leading to irregular menstrual cycles, decreased libido, and fertility issues.
- Insulin: Stress can also influence insulin levels, potentially leading to imbalances in blood sugar regulation.
The Role of Cortisol in Stress Response
Cortisol is a hormone produced by the adrenal glands that plays a crucial role in the body's response to stress. It is often referred to as the "stress hormone" because its levels increase in response to stressors.
Function of Cortisol
Cortisol helps regulate metabolism, reduce inflammation, and assist in memory formation. It also plays a role in controlling blood sugar levels, regulating blood pressure, and influencing the immune system. In times of stress, cortisol helps the body respond by mobilizing energy and resources to deal with the perceived threat.
Triggering Cortisol Release
When the body perceives stress, whether physical or psychological, the hypothalamus in the brain signals the pituitary gland to release adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). ACTH then stimulates the adrenal glands to produce cortisol. This process is known as the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, which is the body's central stress response system.
Effects of Elevated Cortisol Levels
Chronic stress can lead to prolonged elevation of cortisol levels in the body, which can have detrimental effects on hormonal health. High cortisol levels over time can disrupt the balance of other hormones in the body, such as insulin, thyroid hormones, and reproductive hormones.
This imbalance can contribute to conditions like insulin resistance, thyroid disorders, and menstrual irregularities.
Impact of Stress on Sex Hormones
Stress can have a significant impact on the production and balance of sex hormones in the body, leading to various reproductive health issues.
Effect on Sex Hormone Production
- Chronic stress can disrupt the normal production of sex hormones such as estrogen and testosterone.
- This imbalance can result in irregular menstrual cycles in women and decreased libido in both men and women.
- High levels of stress can also lead to lower sperm count and decreased sperm motility in men.
Link to Irregular Menstrual Cycles
- Stress can disrupt the delicate balance of hormones involved in the menstrual cycle, leading to irregular periods.
- Increased levels of cortisol, the stress hormone, can interfere with the production of estrogen and progesterone, affecting the timing and regularity of menstrual cycles.
- Women experiencing chronic stress may face difficulties in conceiving due to these hormonal imbalances.
Connection to Reproductive Health Issues
- Chronic stress has been linked to a higher risk of reproductive health issues such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and infertility.
- Stress can impact the functioning of the hypothalamus-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis, which regulates reproductive hormones.
- Imbalances in sex hormone levels due to stress can contribute to conditions like endometriosis and erectile dysfunction.
Thyroid Function and Stress
Stress not only affects sex hormones and cortisol but can also have a significant impact on thyroid function. The thyroid gland plays a crucial role in regulating hormones that control metabolism, energy production, and overall body functions.
Role of the Thyroid Gland in Hormone Regulation
The thyroid gland produces hormones such as thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which are essential for regulating metabolism, body temperature, and heart rate. These hormones are involved in almost every process in the body, from digestion to mood regulation.
- The thyroid hormones T4 and T3 are responsible for maintaining the body's energy levels and metabolism.
- Thyroid hormones also play a key role in the growth and development of tissues and organs.
- Proper thyroid function is vital for maintaining overall health and well-being.
How Stress Can Disrupt Thyroid Function
When the body is under stress, the adrenal glands release cortisol in response to the perceived threat. Prolonged stress can lead to imbalances in cortisol levels, which can disrupt the delicate balance of thyroid hormones.
- High levels of cortisol can inhibit the conversion of T4 to the active form T3, leading to hypothyroidism.
- Chronic stress can also suppress the production of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) from the pituitary gland, further impacting thyroid function.
- Stress-induced inflammation can also affect the thyroid gland directly, causing thyroid dysfunction.
Implications of Stress-Induced Thyroid Imbalances on Overall Health
Thyroid imbalances caused by stress can have far-reaching effects on overall health and well-being. An underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism) can lead to symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain, depression, and cognitive difficulties. On the other hand, an overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism) can result in symptoms like anxiety, weight loss, and heart palpitations.
- Untreated thyroid imbalances can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease, infertility, and other serious health conditions.
- Managing stress through lifestyle changes, relaxation techniques, and proper nutrition is crucial for maintaining optimal thyroid function and overall hormonal health.
- Regular monitoring of thyroid function through blood tests can help detect imbalances early and prevent long-term health complications.
Gut-Brain Axis and Hormonal Health
The gut-brain axis refers to the bidirectional communication system between the gastrointestinal tract and the brain. This complex relationship plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, including the regulation of hormones and response to stress.
Impact of Stress on Gut Health and Hormonal Balance
Chronic stress can disrupt the balance of beneficial bacteria in the gut, leading to issues such as inflammation, leaky gut syndrome, and impaired digestion. These disruptions can, in turn, affect the production and regulation of hormones in the body, contributing to hormonal imbalances.
- Stress-induced changes in the gut microbiota composition can impact the production of neurotransmitters and hormones involved in mood regulation and stress response.
- Increased gut permeability caused by stress can lead to the leakage of toxins into the bloodstream, triggering an immune response and further exacerbating hormonal dysregulation.
- Imbalances in gut bacteria due to chronic stress have been linked to conditions such as adrenal fatigue, thyroid disorders, and reproductive hormone imbalances.
Strategies to Support Gut Health for Improved Hormonal Regulation in Times of Stress
Taking steps to support gut health can help mitigate the negative effects of stress on hormonal balance and overall well-being.
- Follow a balanced diet rich in fiber, probiotics, and prebiotics to promote a healthy gut microbiota.
- Manage stress through relaxation techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, and yoga to reduce the impact on gut health.
- Stay hydrated, exercise regularly, and get an adequate amount of sleep to support overall gut function and hormone regulation.
- Consider adding supplements like probiotics, digestive enzymes, and adaptogenic herbs to support gut health and resilience to stress.
Closing Summary
In conclusion, it's evident that stress plays a significant role in shaping our hormonal health. By understanding these connections, we can take proactive steps to manage stress and support our hormones for overall well-being.
FAQ
Can stress directly affect hormone production?
Yes, stress can disrupt hormone production by triggering the release of cortisol, which can impact various hormonal balances in the body.
Is there a connection between stress and thyroid function?
Absolutely, stress can interfere with thyroid function, leading to imbalances that affect overall health and hormonal regulation.
How does stress impact gut health and hormonal balance?
Stress can disrupt the gut-brain axis, affecting gut health and potentially leading to hormonal imbalances.
Can stress cause irregular menstrual cycles in women?
Yes, stress can be a contributing factor to irregular menstrual cycles in women due to its impact on sex hormone production.